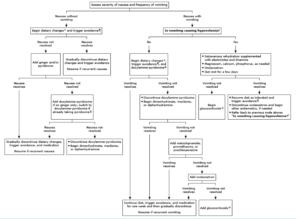
Treatment for Hyperemesis gravidarum
Management of nausea without vomiting
- begin dietary changes and avoid trigger
- if nausea does not improve then add pyridoxine and if symptoms still persistent then add doxylamine pyridoxine
- However, if the vomiting does not resolve then discontinue doxylamine pyridoxine and begin either Dimenhydrinate, meclizine, and diphenhydramine if the vomiting resolves then continue diet changes, avoid triggers and continue medication one more week and then gradually discontinue
Management of vomiting without hypovolemia
- First begin dietary changes and doxylamine pyridoxine and if the vomiting resolves then continue diet changes, avoid triggers and continue medication one more week and then gradually discontinue
- However if the vomiting does not resolve then discontinue doxylamine pyridoxine and begin either Dimenhydrinate, meclizine, and diphenhydramineand if the vomiting resolves then continue diet changes, avoid triggers and continue medication one more week and then gradually discontinue
- If vomiting still continue then add metoclopramide, promethazine or prochlorperazine and if that still does not work then add ondansetron and the final resources will be to add glucocorticoids
Management of vomiting with symptoms of hypovolemia lassitude, postural dizziness, thirst, tachycardia, decreased urine volume and frequency
- IV rehydration with electrolytes and thiamine
- We correct hypovolemia with up to 2 L intravenous Ringer’s lactate infused over three to five hours, supplemented with appropriate electrolytes and vitamins.
- After initial replacement fluid therapy with Ringer’s lactate, we administer dextrose 5 percent in 0.45 percent saline with 20 mEq potassium chlorideat 150 mL/hour to patients with normal potassium levels
- Magnesium, calcium and phosphorus as needed
Pharmacological treatment:
- Add ondansetron 4 to 8 mg intravenously (IV push) once every eight hours upon hospitalization for intravenous fluid therapy. Once the patient is stabilize discontinue the ondansetron
- Intravenous dimenhydrinate 50 mg every four to six hours, metoclopramide5 to 10 mg every eight hours, or promethazine5 to 25 mg every four to six hours is an alternative to ondansetron
- If ondansetron (Zofran) does not work then add glucocorticoids
Patient Education
- Eat as soon as you feel hungry, or even before you feel hungry.
- Snack often and eat small meals. The best foods to eat are high in protein or carbohydrates, and low in fat. These include crackers, bread, pretzels, nuts, and low-fat yogurt.
- Avoid foods that are spicy, greasy, or acidic (such as oranges).
- Drink cold, clear beverages, such as sports drinks and ginger ale. Avoid coffee. Also, try to drink between meals, rather than with a meal.
- Suck on popsicles or ginger-flavored lollipops.
- Brush your teeth right after you eat.
- Avoid lying down right after you eat.
- Take your vitamins at bedtime with a snack, not in the morning
Sources: